Scientific Units
Last Updated: 10/26/20 by Tim Paschkewitz
1The International System (SI) of Units
Many general-purpose spreadsheet and plotting tools are intended for business or financial applications and do not support the concept of scientific units. AfterMath, however, is a tool designed specifically to meet the needs of scientists and engineers, and one of its distinguishing features is the ability to keep track of proper scientific measurement units.
Internally, AfterMath explicitly associates all numeric data with a scientific unit derived from the International System of Units (SI System)
 Wikipedia - International System of Units (SI)
. This system is based on seven fundamental units of measure, as shown in Table 1:
Wikipedia - International System of Units (SI)
. This system is based on seven fundamental units of measure, as shown in Table 1:
| Name | Symbol | Quantity |
| meter | length | |
| kilogram | mass | |
| second | time | |
| Ampere | electric current | |
| Kelvin | temperature | |
| mole | amount of substance | |
| candela | luminous intensity |
Table 1. Seven Fundamental SI Units of Measure
AfterMath recognizes these seven fundamental units of measure and also many other units of measure that are derived from these seven units. These fundamental and derived SI units may be used in conjunction with the following standard metric prefixes:
| 1000m | 10n | Prefix | Symbol | Short Scale | Long Scale | Decimal |
| yotta- | Y | Septillion | Quadrillion | 1 000 000 000 000 000 000 000 000 | ||
| zetta- | Z | Sextillion | Trilliard | 1 000 000 000 000 000 000 000 | ||
| exa- | E | Quintillion | Trillion | 1 000 000 000 000 000 000 | ||
| peta- | P | Quadrillion | Billiard | 1 000 000 000 000 000 | ||
| tera- | T | Trillion | Billion | 1 000 000 000 000 | ||
| giga- | G | Billion | Milliard | 1 000 000 000 | ||
| mega- | M | Million | 1 000 000 | |||
| kilo- | k | Thousand | 1 000 | |||
| hecto- | h | Hundred | 100 | |||
| deca- | da | Ten | 10 | |||
| 10000 | 100 | (none) | (none) | One | 1 | |
| deci- | d | Tenth | 0.1 | |||
| centi- | c | Hundredth | 0.01 | |||
| milli- | m | Thousandth | 0.001 | |||
| micro- | µ | Millionth | 0.000 001 | |||
| nano- | n | Billionth | Milliardth | 0.000 000 001 | ||
| pico- | p | Trillionth | Billionth | 0.000 000 000 001 | ||
| femto- | f | Quadrillionth | Billiardth | 0.000 000 000 000 001 | ||
| atto- | a | Quintillionth | Trillionth | 0.000 000 000 000 000 001 | ||
| zepto- | z | Sextillionth | Trilliardth | 0.000 000 000 000 000 000 001 | ||
| yocto- | y | Septillionth | Quadrillionth | 0.000 000 000 000 000 000 000 001 | ||
Table 2. SI System Prefixes
2Non-SI Units
There are several units of measurement still in use by scientists and engineers that are not part of the SI system. AfterMath recognizes some (but not all) of these non-SI units. For example, the plot "Displacement vs. Time" shown in Figure 1 gives the distance in feet (an English unit) versus time in hours (rather than seconds). Even in this case, however, it is important to note that AfterMath stores the data internally in the appropriate SI units (meters and seconds). But for display purposes, the data is automatically scaled to match the non-SI units that were chosen for this plot (feet and hours).
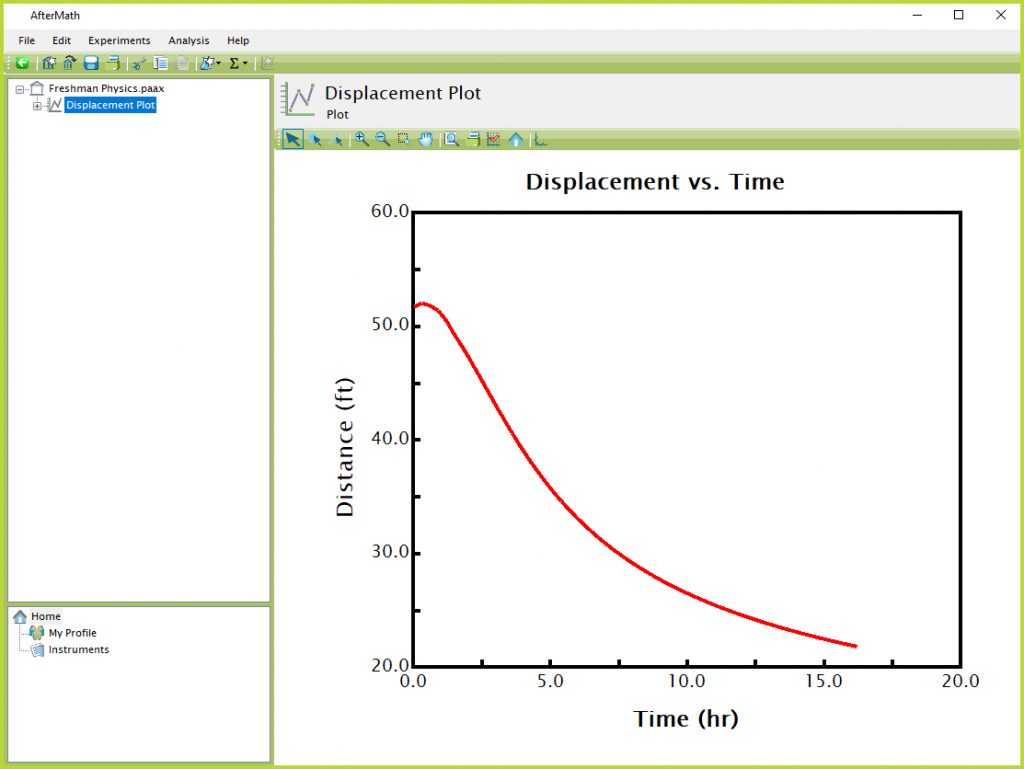
Figure 1. AfterMath Plot with Non-SI Units
Finally, AfterMath also permits the use of unitless data when necessary.



