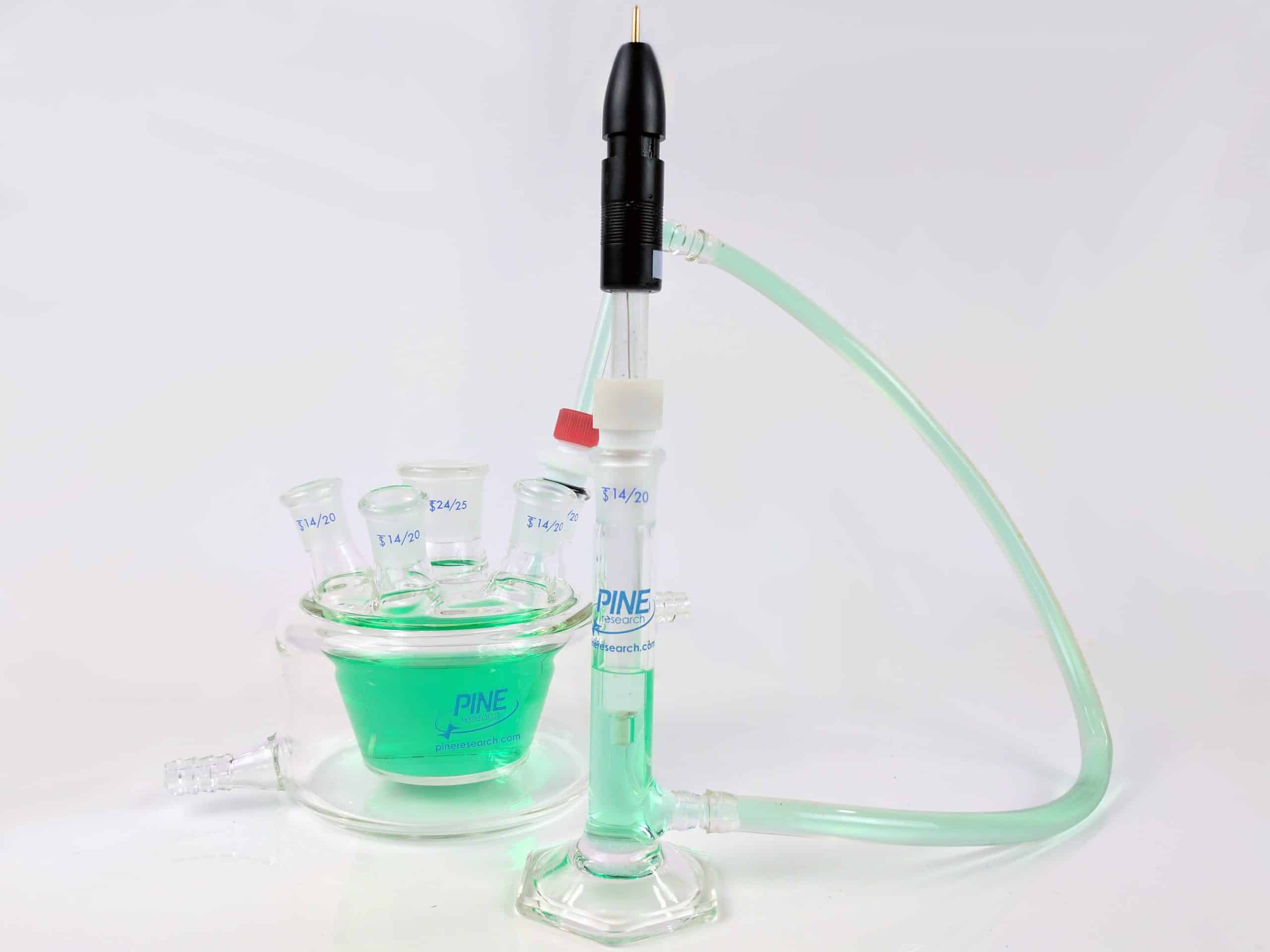
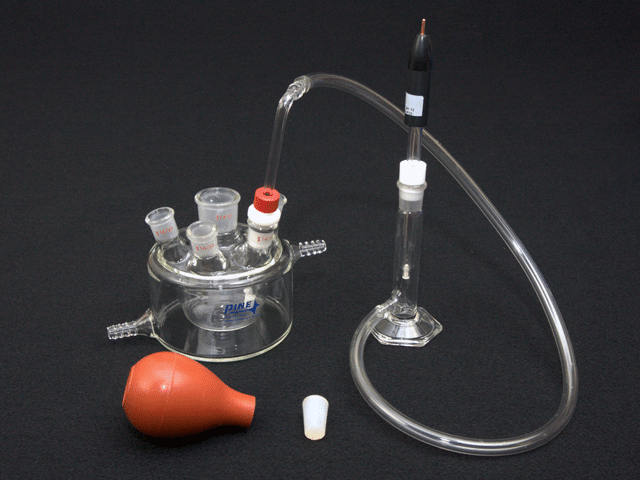
Reference Electrode Salt Bridge Kit
Part Number
AKTUBE1420
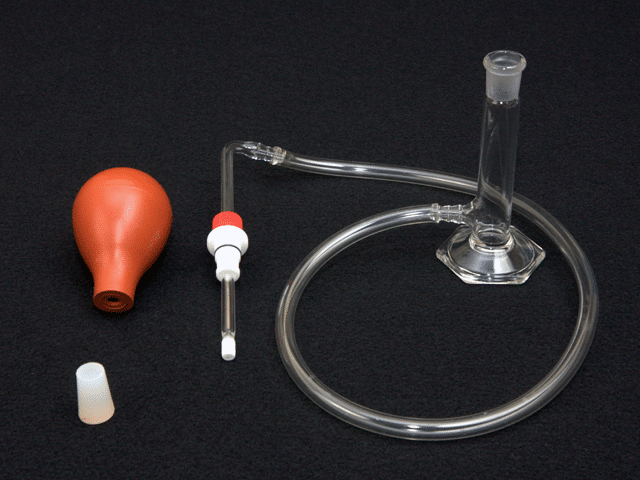
This salt bridge kit is used to physically and diffusionally isolate the reference electrode from the bulk solution. The salt bridge kit offers a conductive connection between the electrochemical cell (bulk solution) and a separate beaker containingthe same solution. Reference electrode instability is often caused by a high solution temperature or by a chemical or physical process that plugs the frit at the tip of the reference electrode.
Login to View Prices
Customers must be logged into their account to view prices. Not all regions provide pricing online. If you do not see prices, you can obtain them from the designated sales channel in your region.