General Electrochemistry
Back to General Electrochemistry Back to Applications Back to Knowledgebase Home1Overview
2Electrical Isolation Guide
| Letter | Color | Description |
| A | Red | Rotator connection section of shaft (electrically-isolated) |
| B | Blue | Disk/cylinder electrical connection section of shaft |
| C | Green | Ring electrical connection section of shaft |
| D | Blue | Disk electrical connection section of an RDE/RRDE tip |
| E | Blue | RDE and/or RRDE electrode tip disk/RCE cylinder |
| F | Green | Ring electrical connection section of an RRDE tip |
| G | Green | RRDE electrode tip ring |
3Rotating Ring-Disk Electrodes (RRDE)
3.1Electrical Test for AFE6M/AFE6MB Shaft
- The resistance between A and B should be infinity
- The resistance between B and C should be infinity
- The resistance between A and C should be infinity
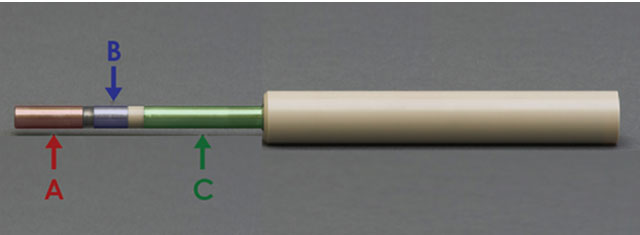
Figure 1. RRDE Shaft with Electrically-Isolated Sections Labeled
3.2Electrical Test for Rotating Ring-Disk Electrode Tips (E6, E7, and E8 Series)
- The resistance between D and E should be less than 10 Ω
- The resistance between F and G should be less than 10 Ω
- The resistance between D and F should be infinity
- The resistance between E and G should be infinity
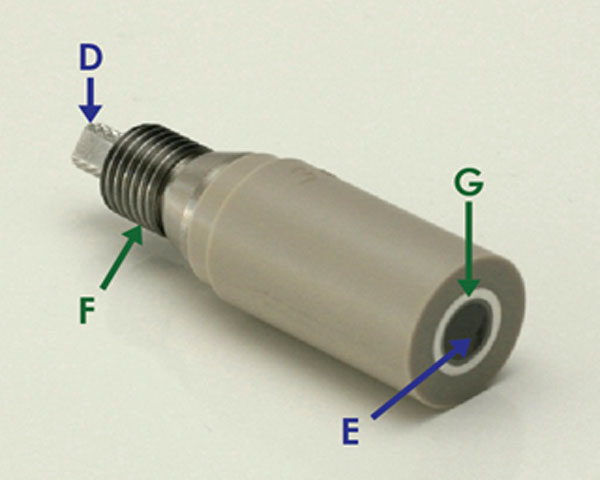
Figure 2. RRDE Tip with Electrical Connections Labeled
4Rotating Disk Electrodes (RDE)
4.1Electrical Test for AFE3M Shaft
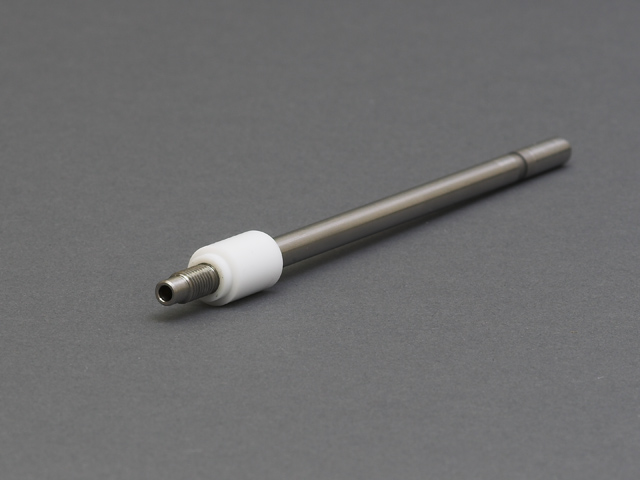 Standard 12 mm RDE/RCE Shaft
has two electrically-isolated sections, A and B (see Figure 3). Section A of the shaft connects to the rotator while section B connects to the disk. The resistance between these sections should be infinity. To test the shaft, use a multimeter to measure the resistance between the connections, as follows:
Standard 12 mm RDE/RCE Shaft
has two electrically-isolated sections, A and B (see Figure 3). Section A of the shaft connects to the rotator while section B connects to the disk. The resistance between these sections should be infinity. To test the shaft, use a multimeter to measure the resistance between the connections, as follows:- The resistance between A and B should be infinity
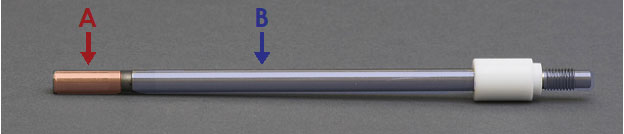
Figure 3. RDE Shaft with Isolated Electrical Connections Labeled
4.2Electrical Test for RDE Tips (E3, E5, E5TQ, and E6TQ Series)
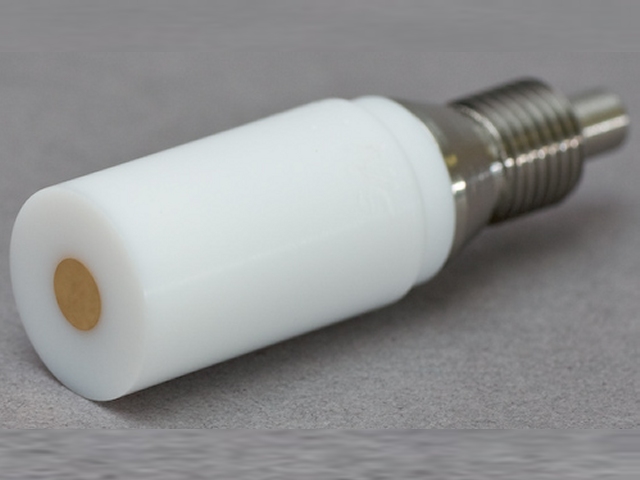
 E3 Fixed-Disk RDE Tips PTFE
and 15 mm OD (E5,
E3 Fixed-Disk RDE Tips PTFE
and 15 mm OD (E5,
 E5 Fixed-Disk RDE Tips PTFE
E5TQ,
E5 Fixed-Disk RDE Tips PTFE
E5TQ,
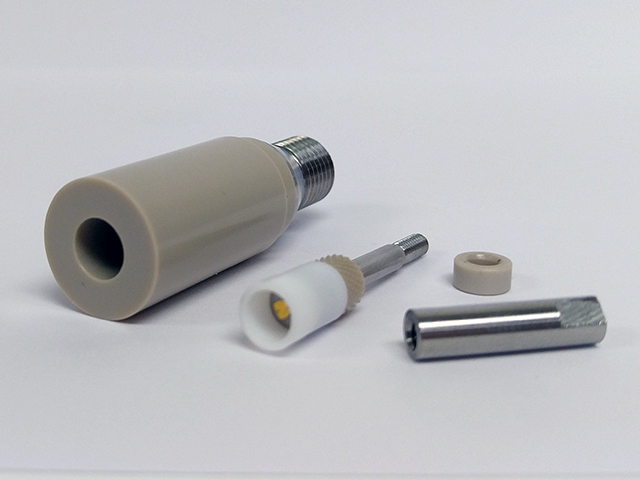
 E5TQ ChangeDisk RDE Tip PTFE
and E5TQPK
E5TQ ChangeDisk RDE Tip PTFE
and E5TQPK
 E5TQ ChangeDisk RDE Tip PEEK
series). For the 12 mm OD tip, the disk electrode E is electrically-coupled to the female threading D (see Figure 4a and Figure 4b). For the 15 mm OD tip, the disk electrode E is electrically-coupled to threaded pin D (see Figure 4c). The resistance between D and E of RDE tips should be fairly small. Use a multimeter to measure the resistance between these connections, as follows.
E5TQ ChangeDisk RDE Tip PEEK
series). For the 12 mm OD tip, the disk electrode E is electrically-coupled to the female threading D (see Figure 4a and Figure 4b). For the 15 mm OD tip, the disk electrode E is electrically-coupled to threaded pin D (see Figure 4c). The resistance between D and E of RDE tips should be fairly small. Use a multimeter to measure the resistance between these connections, as follows.- The resistance between D and E on the shaft should be less than 10 Ω
- The resistance between D and E on the shaft should be less than 10 Ω
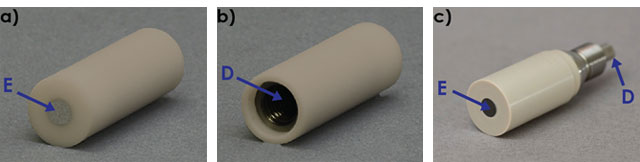
Figure 4. a) Front and b) Back of a 12 mm OD RDE tip and c) a 15 mm OD RDE Tip Showing Electrical Isolation
5Rotating Cylinder Electrodes (RCE)
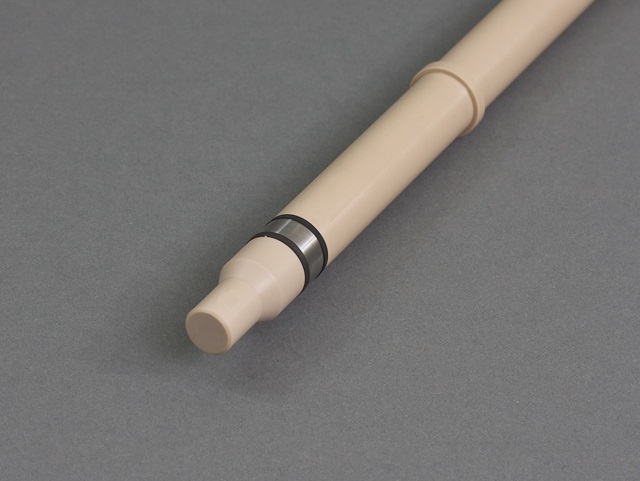 Precision 15 mm Single RCE Shaft
and AFE3M,
Precision 15 mm Single RCE Shaft
and AFE3M,
 Standard 12 mm RDE/RCE Shaft
respectively). The latter shaft, AFE3M, was discussed in section 4.1.
Standard 12 mm RDE/RCE Shaft
respectively). The latter shaft, AFE3M, was discussed in section 4.1. 5.1Electrical Test for AFE9MBA Shaft
 Precision 15 mm Single RCE Shaft
shaft has two electrically-isolated sections, A and B (see Figure 5). Section A of the shaft connects to the rotator while section B connects to the cylinder. The resistance between these sections should be infinity. To test the shaft, use a multimeter to measure the resistance between the connections, as follows:
Precision 15 mm Single RCE Shaft
shaft has two electrically-isolated sections, A and B (see Figure 5). Section A of the shaft connects to the rotator while section B connects to the cylinder. The resistance between these sections should be infinity. To test the shaft, use a multimeter to measure the resistance between the connections, as follows:- The resistance between A and B should be infinity

Figure 5. RCE Shaft with Electrically-Isolated Sections Labeled
5.2Electrical Test for 15 mm RCE Tips (E9 Series)
- The resistance between A and E should be infinity
- The resistance between B and E should be less than 10 Ω

Figure 6. Electrical Isolation Labeled with Cylinder Inserted on Shaft AFE9MBA
5.3Electrical Test for 12 mm RCE Tips (ACQC Series)
- The resistance between D and E should be less than 10 Ω

Figure 7. RCE Shaft with Electrically-Isolated Sections Labeled



