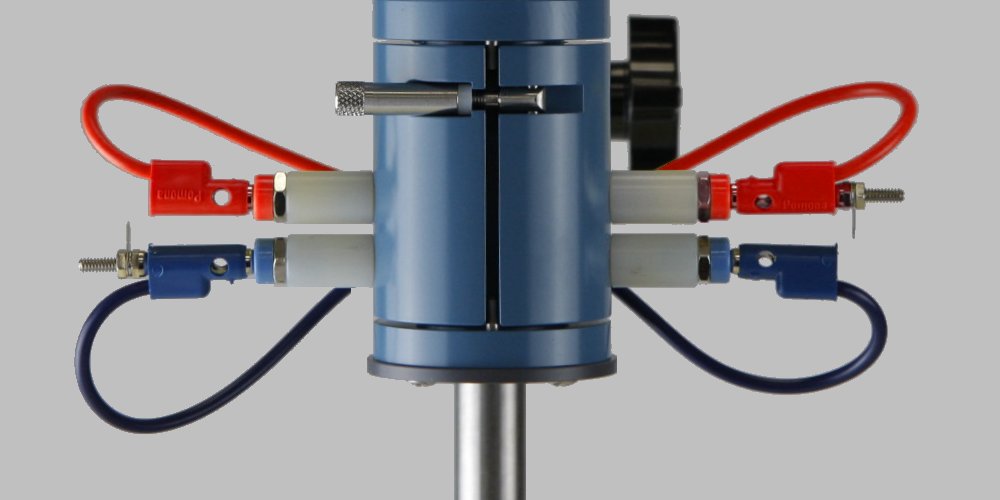
WARNING:
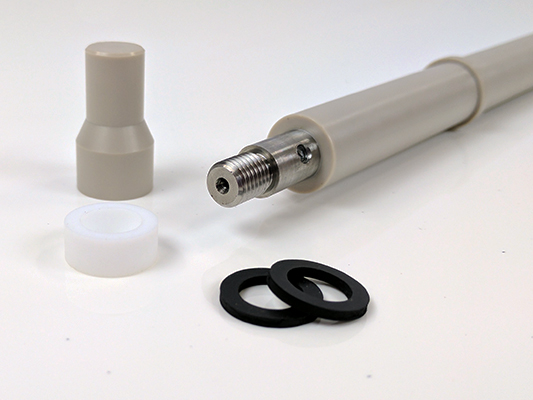
Do not use or attempt to rotate an electrode shaft that has been dropped, bent or otherwise physically damaged.
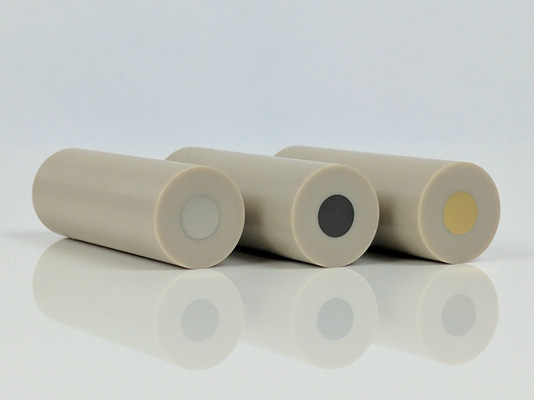
Inspect the shaft to be certain that it is not damaged.
AVERTISSEMENT:
N’utilisez pas et ne tentez pas de mettre en rotation un arbre d’électrode qui est tombé, a été tordu ou a été endommagé physiquement d’une autre manière ou d’une autre.
Inspectez l’arbre pour vous assurer qu’il n’a pas été endommagé.

WARNING:
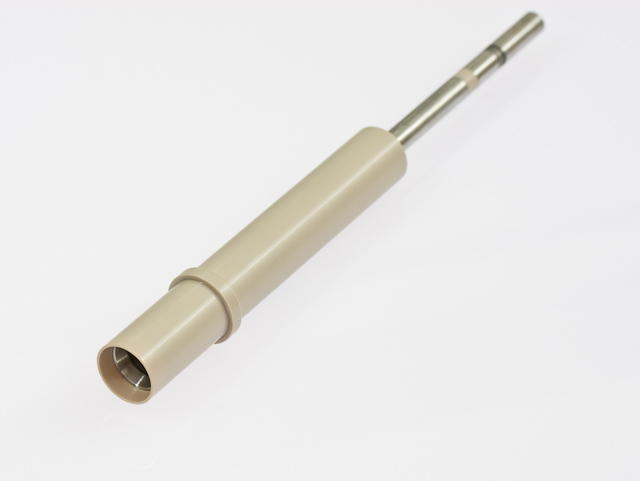
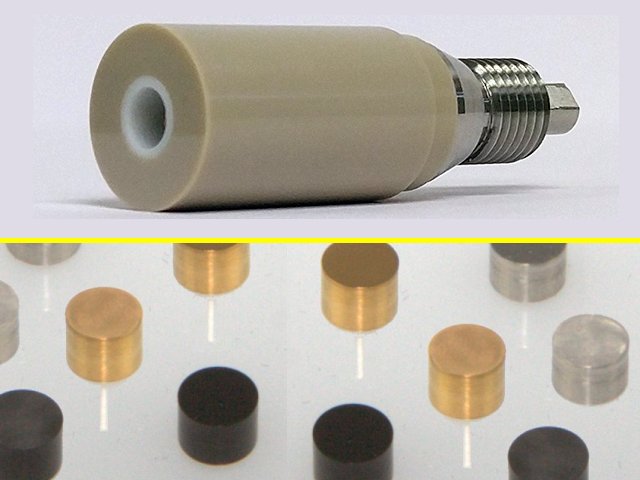
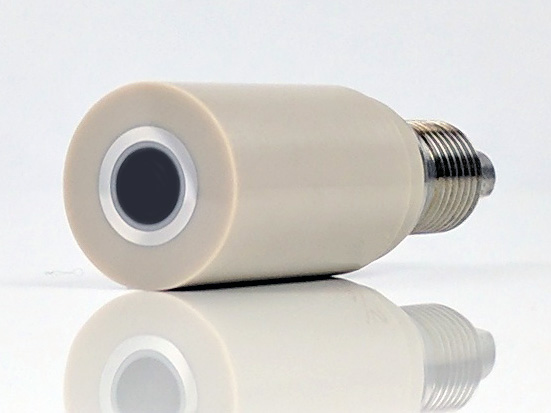
Do not use or attempt to rotate an electrode tip that has been dropped or otherwise physically damaged.
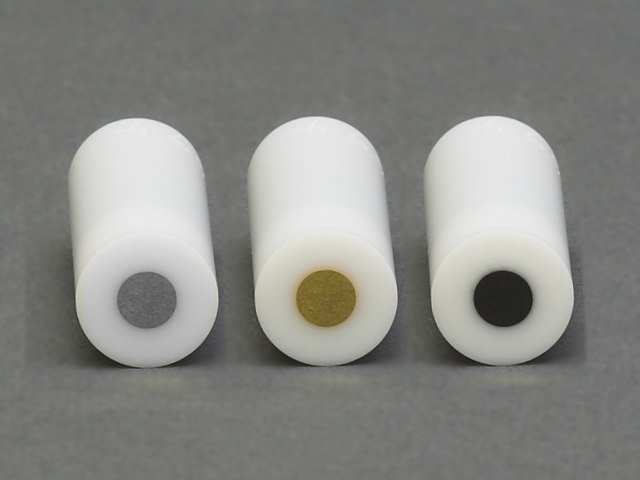
Inspect the electrode tip to be certain that it is not damaged.
AVERTISSEMENT:
N’utilisez pas et ne tentez pas de mettre en rotation un embout d’électrode qui est tombée ou a été endommagée physiquement d’une autre manière ou d’une autre.
Inspectez l’embout d’électrode pour vous assurer qu’elle n’a pas été endommagée.

WARNING:
Do not use an electrode shaft which appears to wobble, vibrate, or tilt away from the axis of rotation while rotating. Such a shaft is either improperly installed or physically damaged. Turn off the rotator, disconnect electrical power, and remove the shaft immediately.
AVERTISSEMENT:
N’utilisez pas un arbre d’électrode qui semble osciller, vibrer ou dévier de l’axe de rotation pendant la rotation. Cet arbre est soit installé de manière incorrecte soit endommagé physiquement. Éteignez le rotateur, déconnectez l’alimentation électrique et retirez l’arbre immédiatement.

WARNING:
Do not use an electrode tip which appears to wobble, vibrate, or tilt away from the axis of rotation while rotating. Such an electrode tip is either improperly installed or physically damaged. Turn off the rotator, disconnect electrical power, and remove the electrode tip immediately.
AVERTISSEMENT:
N’utilisez pas un embout d’électrode qui semble osciller, vibrer ou dévier de l’axe de rotation pendant la rotation. Cet embout d’électrode est soit installée de manière incorrecte soit endommagée physiquement. Éteignez le rotateur, déconnectez l’alimentation électrique et retirez l’embout d’électrode immédiatement.

CAUTION:
Do not exceed the maximum rotation rate for an electrode.
Each type of rotating electrode has a specific maximum rotation rate limitation. Consult the documentation for the specific electrode being used in order to learn the maximum rotation rate for that electrode.
ATTENTION:
Ne dépassez pas la vitesse de rotation maximum pour une électrode.
Chaque type d’électrode rotative possède une vitesse de rotation maximum spécifique.
Consultez la documentation pour l’électrode spécifique à utiliser pour connaître la vitesse de rotation maximum de l’électrode.

CAUTION:
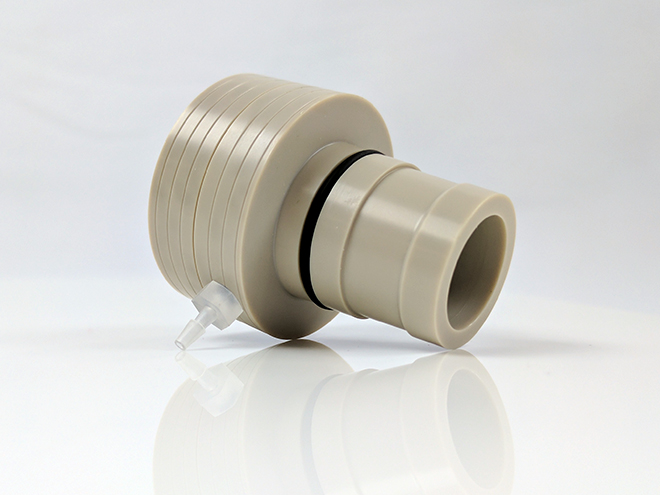
Do not apply excessive twisting force to the shroud of an electrode tip when threading it on to the shaft, as this may cause a leak between the shroud and the electrode.
ATTENTION:
N’appliquez pas une force de torsion excessive à l’enveloppe de protection d’un embout d’électrode lorsque vous la vissez sur l’arbre, car cela pourrait provoquer une fuite entre l’enveloppe de protection et l’électrode.

CAUTION:
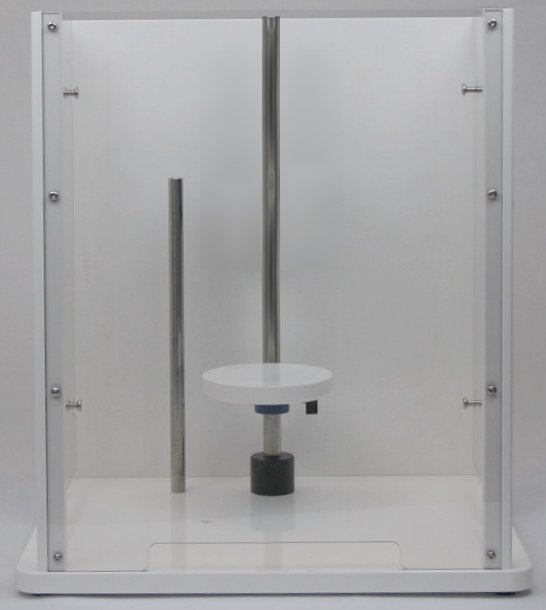
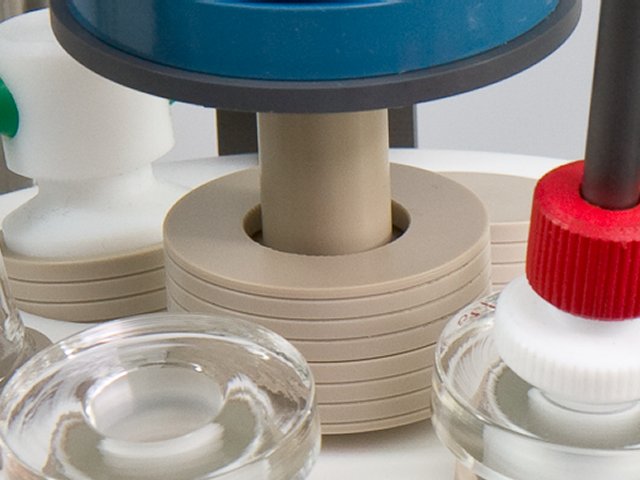
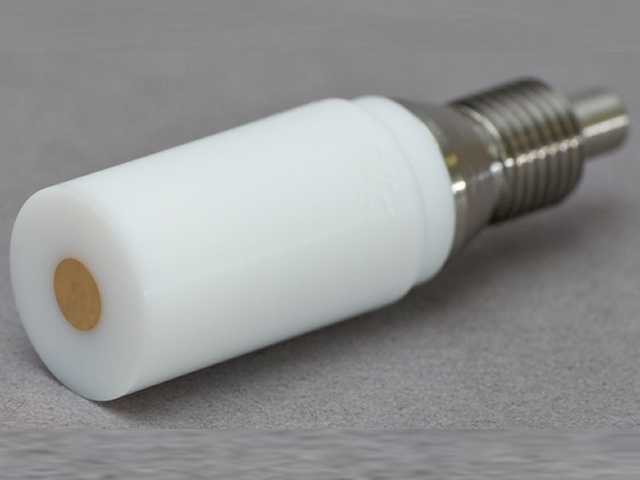
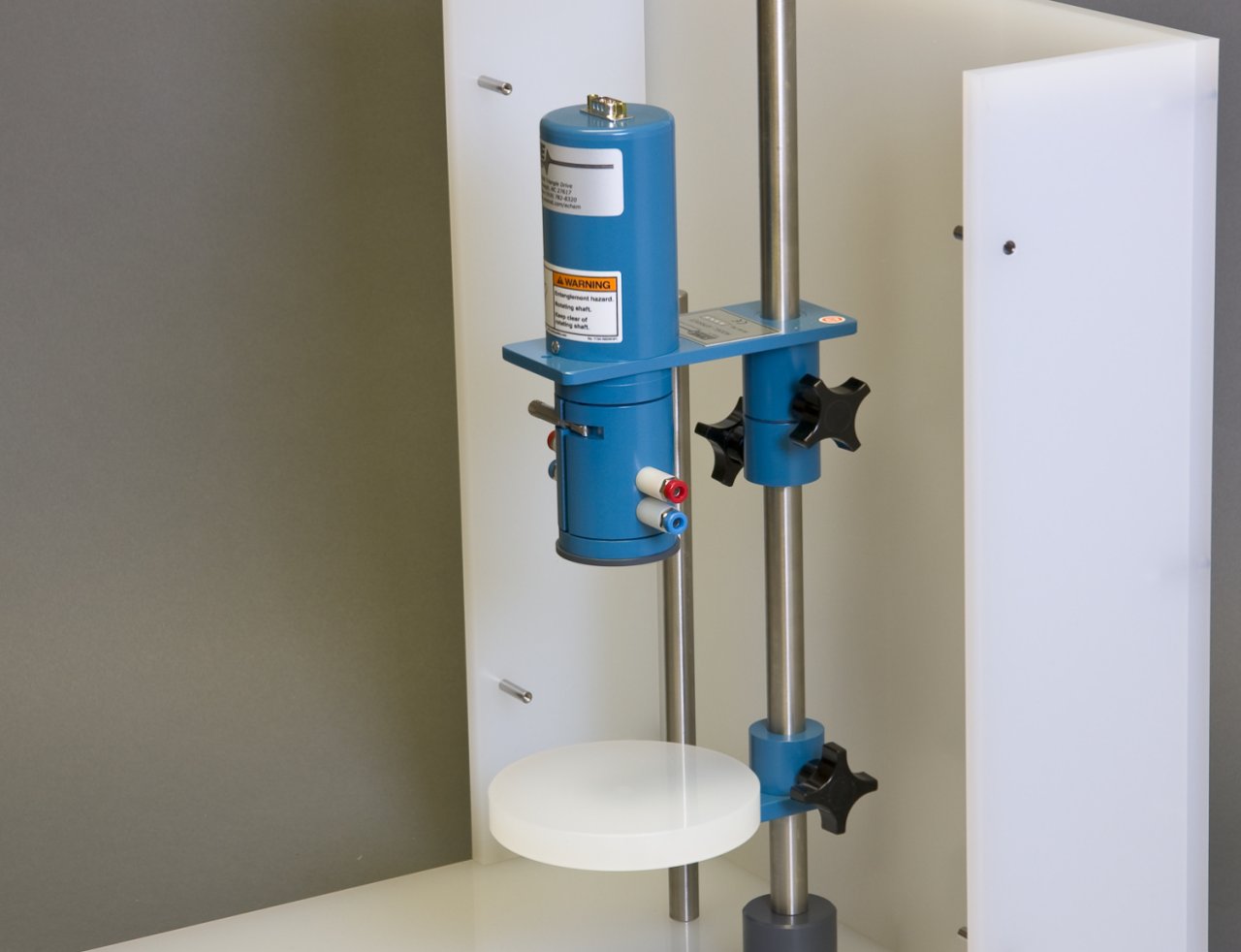
Position the motor unit with respect to the glass cell so that the electrode tip is immersed approximately 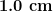 into the test solution.
into the test solution.
Excessive immersion may corrode the shaft or tip by allowing liquids to seep into the joint between the shaft and tip.
ATTENTION:
Positionnez le bloc moteur en fonction de la position de la cellule de verre, de telle sorte que l’embout d’électrode soit immergée sur environ 1 cm dans la solution d’essai.
Une immersion excessive peut entraîner la corrosion de l’arbre ou d’embout d’électrode en provoquant l’infiltration de liquides dans le joint situé entre l’arbre et l’embout d’électrode.

CAUTION:
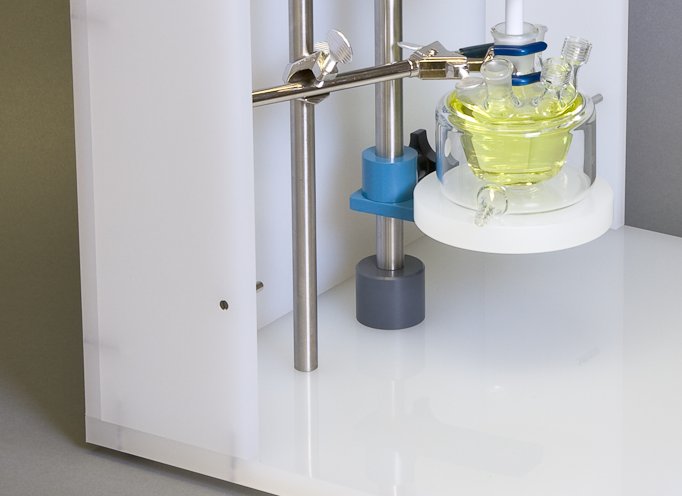
Center the rotating electrode within the opening on the cell so that it does not rub against the walls of the opening.
Damage will occur if the rotating shaft or tip abrades against these walls.
ATTENTION:
Centrez l’électrode rotative dans l’ouverture de la cellule pour qu’elle ne frotte pas les bords de l’ouverture.
Le frottement des bords de la cellule par l’arbre ou par l’embout d’électrode entraînera des dommages.
 TEMPERATURE LIMITATIONS:
TEMPERATURE LIMITATIONS:
Electrode tips with PTFE shrouds are designed for use at room temperature (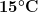 to
to 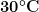 ). Exposing these tips to colder or warmer temperatures is likely to compromise the seal between the PTFE shroud and the electrode surface.
). Exposing these tips to colder or warmer temperatures is likely to compromise the seal between the PTFE shroud and the electrode surface.
Electrode tips with PEEK or PCTFE shrouds are available and are better suited for use at elevated temperatures.
 NOTE:
NOTE:
After each use of rotating electrode (or electrode tip), clean and dry the electrode and then return it to the plastic storage box in which it was originally shipped.
 NOTE:
NOTE:
A polishing kit is available for use in restoring the electrode surface to its original mirror smooth finish. A slurry of microscopic abrasive particles may be used to routinely repolish the electrode surface (usually at the end of each day). In the event of very serious damage to the electrode surface, it is generally better to return the electrode to the factory for professional repolishing.